What is a Heat Pump?
As it is known, energy cannot be created from nothing, it can only change form or move from one place to another (1st law of thermodynamics).
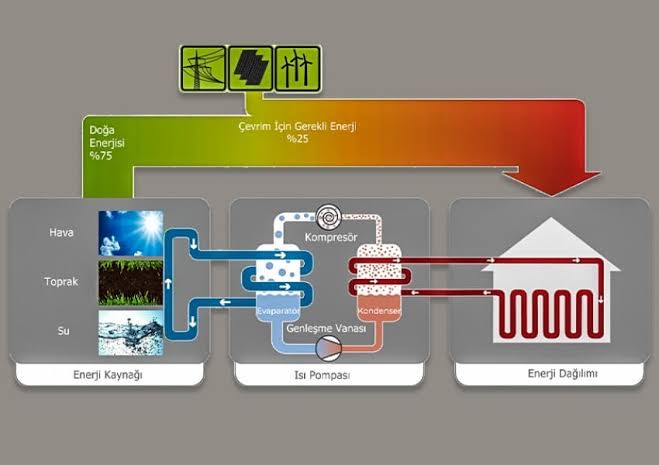
Heat pumps are devices that extract natural heat from the environment and then convert and pump it to a higher temperature and pressure where it can be used to provide heating, cooling and domestic hot water to your home.
The heat pump uses energy found in nature and produces 100% heating energy, 75% from nature, with an average of 25% electrical energy
This medium can be air, water or soil. In this way, there are three types of heat pumps: air source, water source and ground source.
Heat pump technology is the most effective air conditioning solution. The main reason for this is that while fossil fuel heating systems generate heat as a result of a chemical reaction, heat pumps transfer the heat that exists on earth. It is also environmentally friendly as it works without using fossil fuels and does not release harmful gases into the environment.
What is the Working Principle of the Heat Pump?
Specifically, the heat extracted from the sources is transferred to a heat exchanger (evaporator) mounted on the heat pump. At this point, the physical state of the refrigerant circulating in the cycle changes with the energy it receives from the source and evaporation occurs even at low temperatures. This gaseous fluid is then compressed by a compressor to raise it to a level that can be used for heating and hot water production.
After this stage, heat is transferred from the high temperature and high pressure fluid to the heating and hot water circuits in your home, again through a heat exchanger (condenser). Thanks to their highly effective and efficient design, these solutions can generate heat even when the temperature outside is as low as -15°C.